Emissions
Emissions - Basic Overview
A set of introductory slides on air pollution emissions and control technologies has been provided, courtesy of Dr. Christian Seigneur. These slides are the basis of his 2019 book: Air Pollution - Concepts, Theory, and Applications.
Read More →Odor Sources and Emissions
The techniques used for sampling odors from different sources and estimating the emission rates is discussed in Section 4 (page 111) of the International Handbook on the Assessment of Odour Exposure using Dispersion Modelling.
Read more →Urban Emission (Italy, 17th Century)
This Note presents an article (Archaeometry of Air Pollution: Urban Emission in Italy during the 17th Century) prepared by Prof. Dario Camuffo who has studied ancient emission records.
Read more →Air Quality Impact of Wildland Fires
The smoke produced during wildland fires is one of the most disturbing consequences of these events with large amounts of gaseous and particulate (e.g., PM10) compounds emitted to the atmosphere and strongly impacting air quality and human health.
Read more →Transportation - High and Super-High Emitters
These slides present a basic introduction to the issue of high and super-high vehicle emitters of volatile organic carbons, using California data.
Read more →Transportation - Vehicle Refueling Emissions
Slides from the US EPA presenting Refueling Emission Inventories and Regulatory Policy. The presentation was prepared by Glenn W. Passavant, Ingevity Corporation, North Charleston, SC.
Read more →Transportation - Internal Combustion Processes
These slides present a basic introduction to the internal combustion processes used in a motor vehicle burning hydrocarbons and the enormous improvements achieved in the last decades in reducing emissions from volatile organic compounds, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides.
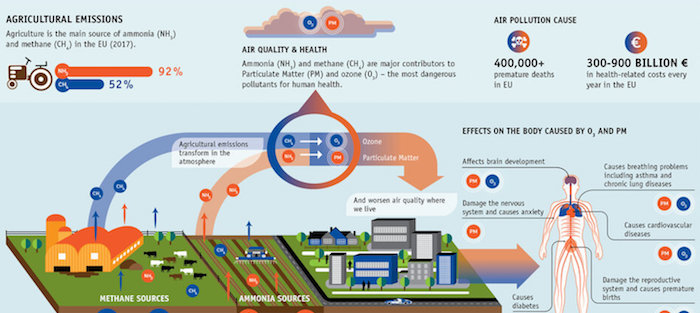
Read more →Anthropogenic Sources - Agriculture
Agriculture is a common driver for both air pollution and climate change. The main greenhouse gases associated with agriculture are CO2 and CH4 from livestock and N2O from crop fields. The main air pollutants related to agricultural activities are NH3 and PM (mainly PM2.5 and PM10).
Read More →Anthropogenic Sources - Landfills
In the U.S., modern landfills are well-engineered and managed facilities for the disposal of solid waste. Landfills are located, designed, operated and monitored to ensure compliance with federal regulations. They are also designed to protect the environment from contaminants, which may be present in the waste stream.
Read More →Anthropogenic Sources - Power Plants
Power plant emissions originate from 1) burning fuel; 2) producing the fuel; and 3) transporting the fuels. The most significant health impacts from producing electricity come from the air emissions from burning fossil fuels, in particular, though not exclusively, from coal-burning power plants.
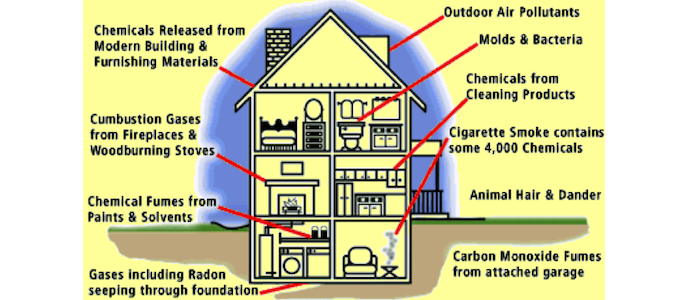
Read More →Anthropogenic Sources - Indoor
A complete introduction to indoor air quality is available at the US EPA site. In particular, the main indoor air pollutants are asbestos, biological pollutants, carbon monoxide, formaldehyde/pressed wood products, lead, and more.
Read More →